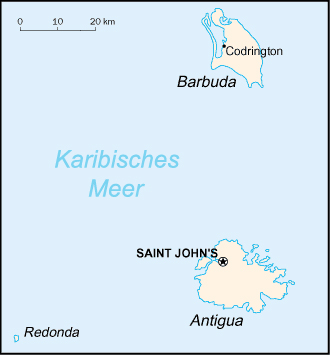
General Antigua and Barbuda is an island nation located in the eastern Caribbean Sea on the boundary with the Atlantic Ocean . Antigua and Barbuda are located in the middle of the Leeward Islands in the Eastern Caribbean , roughly 17 degrees north of the equator. Antigua and Barbuda are part of the Lesser Antilles archipelago with the islands of Guadeloupe , Dominica, Martinique, St. Lucia, St. Vincent & the Grenadines, Barbados, Grenada, Trinidad and Tobago to the south, Montserrat to the southwest, Saint Kitts and Nevis to the west and Saint Barthélemy , Saint Martin and Anguilla to the northwest. |
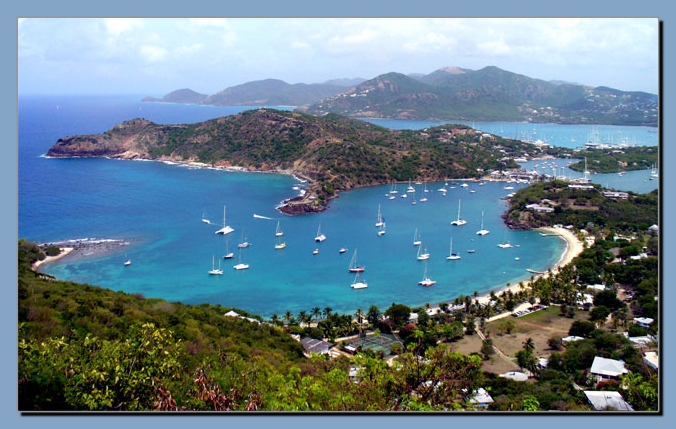
English Harbour - Nelson's Dockyard |
Antigua and Barbuda - Facts
 |
 |
Old Sugar Mill |
HistoryMain article: History of Antigua and Barbuda Pre-ceramic Amerindians were the first to inhabit the islands of Antigua and Barbuda in 2400 BC . Later Arawak and Carib Amerindian tribes populated the islands. The island of Antigua was originally named Wadadli by the natives. Christopher Columbus landed on his second voyage in 1493 and gave the island the name Antigua. Early settlements by the Spanish and French were succeeded by the English who formed a colony in 1667 by transporting Irish Catholic slaves to Antigua. Slavery , established to run the sugar plantations on Antigua, was abolished in 1834. The islands became an independent state within the Commonwealth of Nations on 1 November 1981 , and Vere Bird became the first prime minister .
|
Politics Main articles on politics and government of Antigua and Barbuda can be found at the Politics and government of Antigua and Barbuda series .
Politics of Antigua and Barbuda takes place in a framework of a federal parliamentary representative democratic monarchy , whereby the Prime Minister is the head of government , and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of the Parliament . The Bicameral Parliament consists of the Senate (17-member body appointed by the governor general) and the House of Representatives (17 seats; members are elected by proportional representation to serve five-year terms). The last elections held were on 23 March 2004 for the House of Representatives (next to be held in 2009). The Antigua Labour Party got 4 seats, while the United Progressive Party got 13.  |
Government
Since 1949 the party system had been dominated by the personalist Antigua Labour Party . However the Antigua and Barbuda legislative election, 2004 , saw the defeat of the longest-serving elected government in the Caribbean. The Prime Minister, Lester Bird , had been in office since 1994, when he succeeded his father, Vere Bird . The elder Bird had been Prime Minister from independence in 1981, and before independence had been Chief Minister of Antigua from 1960, except for the period 1971-76.
Structure
The Head of State is the Queen , who is represented by the Governor-General . A Council of Ministers is appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister. The Judicial Branch is the Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court (based in Saint Lucia; one judge of the Supreme Court is a resident of the islands and presides over the Court of Summary Jurisdiction ). Antigua is also a member of the Caribbean Court of Justice . The Supreme Court of Appeal was the British Judicial Committee of the Privy Council , up until 2001, when the nations of the Caribbean Community voted to abolish the right of appeal to the Privy Council in favour of a Caribbean Court of Justice. Some debate between member countries had repeatedly delayed the court's date of inauguration. As of March, 2005, only Barbados was set to replace the process of appeals of Her Majesty in Council with the Caribbean Court of Justice which then had come into operation.
 |
GeographyThe country consists of a number of islands, of which Antigua is the largest one, and the most populated. Barbuda , just north of Antigua is the other main island. The islands have a warm, tropical climate , with fairly constant temperatures year round. Redonda – annexed in the 1860s when Phosphate reserves were noted, unoccupied since 1930 also belongs to the nation of Antigua and Barbuda. The islands are mostly low-lying, with the highest point being Boggy Peak , at 402 metres (1,319 ft ). The small country's main town is the capital Saint John's on Antigua; Barbuda's largest town is Codrington . |
Economy
Manufacturing comprises enclave-type assembly for export with major products being bedding, handicrafts, and electronic components. Prospects for economic growth in the medium term will continue to depend on income growth in the industrialised world, especially in the United States , which accounts for about one-third of all tourist arrivals. |
 |
Demographics Most of the population are descendants of the slaves that used to work in the sugar plantations, but there are also groups of Europeans, notably Irish , British and Portuguese . While the official language is English , most of the locals speak patois,, a form of Creole English. Almost all Antiguans are Christians , with the Anglican Church (about 44%) being the largest denomination. |
Sport Cricket is very popular in Antigua and Barbuda, along with most Commonwealth nations. The 2007 Cricket World Cup will be hosted in the West Indies from 11 March to 28 April 2007. Antigua hopes to host some matches at the Sir Vivian Richards Stadium , which is still under construction, and will hold 20,000 people at full capacity. Football (Soccer) is also a very popular sport and in its season, it seems to be the topic on everyones' mind. Antigua has a national football team but because of lack of experience not much has come out in that sector. |
 |
Cuisine
The national dish is fungie (pronounced foon-gee ) and pepper pot. Fungie is a dish very similar to the Italian Polenta being made mainly of cornmeal. Other local dishes include ducana , season rice, Saltfish and lobster (from Barbuda). There are also local confectionaries which include: sugarcake , fudge, raspberry and tamarind stew and peanut brittle.
Although these foods are indigenous to Antigua and Barbuda and to some other Caribbean countries, the local diet has diversified and now include the local dishes of Jamaica (e.g. jerk pork), Guyana (e.g. Roti) and other Caribbean countries. Chinese restaurants have also begun to become more mainstream. The supermarkets sell a wide variety of food, from American to Italian. Meals also vary depending on social class.
- A typical breakfast in Antigua might include cereal or a sandwich and tea/chocolate milk.
- Lunch might be anything that can be easily bought from a nearby shop, especially a bakery.
- Dinner is definitely the most varied, as it differs depending on taste, social class and education on nutrition. But it will typically include a starch, like rice/macaroni/pasta, vegetables/salad, an entree (fish, chicken, pork, beef etc.) and a side dish like macaroni pie, scalloped potatoes or plantains. Local drinks are mauby , seamoss , tamarind juice, raspberry juice, mango juice, lemonade, coconut milk etc. Adults favor beers and rums, many of which are made locally.
Sunday is the main Sabbath of the country and is the day when the culture is mostly reflected in the food. For breakfast one might have saltfish, eggplant, eggs, bacon, sausages, or lettuce. Dinner on Sundays is eaten earlier (around 2:00 pm) because parents are usually off from work and can stay home and cook. It may include pork, baked chicken, stewed lamb, or turkey, alongside rice (prepared in a variety of ways), macaroni pie, salads, and a local drink. Dessert may be ice cream and cake or an apple pie (mango and pineapple pie in their season) or Jello.
Antiguan Creole (Dialect)
Antiguan Creole is a dialect spoken on the small Caribbean island of Antigua and Barbuda although the Barbudan accent is slightly different.
Persons of higher social status find it easier to switch between Standard English and Antiguan English (dialect) mainly because of better education. The Dialect gets more raw the lower down the socio-economic ladder one moves.
In the years before Antigua and Barbuda's independence (in 1981), Standard English was widely spoken, but after independence, perhaps as a avenue of defiance Antiguan's taught themselves that speaking dialect was a part of their culture and that nothing at all was wrong with it.
Many of the words used in the Antiguan dialect are derived from English and also African origins. The dialect was formed when slaves owned by English planters imitated the English of their masters but failed to pronounce it correctly. This can be easily seen in some phrases like: "Me nah go" meaning "I am not going." And also in: "Ent it?" meaning "Ain't it?" which is in itself dialect and means "isn't it?"
Links:
This website may contain hyperlinks to websites or web pages of third parties or other parties, or refer to them in some other way. Yepton Estate Cottages has no say over the content or other features of these websites or web pages and cannot be held liable in any way for the content or features thereof. Yepton Estate Cottages use of links does not in any way constitute implicit approval of the content of these website or web pages.
- The Official Website of the Government of Antigua and Barbuda
- Antigua & Barbuda , its Department of Tourism website
- Antigua and Barbuda , United States Library of Congress Portals on the World
- Governments on the WWW: Antigua and Barbuda
- The High Commission of Antigua and Barbuda . Tourism, business, history, culture, politics - an up to date website.
- Antigua Carnival - with great photo galleries.
- Informationen i.e. about history, culture and politics
- Extensive Informations about Barbuda
- CIA World Fact Book 2006
- History
Bibliographic details for "Antigua and Barbuda"
- Page name: Antigua and Barbuda
- Author: Wikipedia contributors
- Publisher: Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia .
- Date of last revision: 27 October 2006 14:54 UTC
- Date retrieved: 28 October 2006 09:34 UTC
- Permanent link: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Antigua_and_Barbuda&oldid=84055271
- Primary contributors: View the list (subject to extremely long replication lag)
- Page Version ID: 84055271